The QuEST library API and objects. More...
#include "QuEST_precision.h"Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | ComplexArray |
| Represents an array of complex numbers grouped into an array of real components and an array of coressponding complex components. More... | |
| struct | Complex |
| Represents one complex number. More... | |
| struct | ComplexMatrix2 |
| Represents a 2x2 matrix of complex numbers. More... | |
| struct | Vector |
| struct | MultiQubit |
| Represents a system of qubits. More... | |
| struct | QuESTEnv |
| Information about the environment the program is running in. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct ComplexArray | ComplexArray |
| Represents an array of complex numbers grouped into an array of real components and an array of coressponding complex components. More... | |
| typedef struct Complex | Complex |
| Represents one complex number. More... | |
| typedef struct ComplexMatrix2 | ComplexMatrix2 |
| Represents a 2x2 matrix of complex numbers. More... | |
| typedef struct Vector | Vector |
| typedef struct MultiQubit | MultiQubit |
| Represents a system of qubits. More... | |
| typedef struct QuESTEnv | QuESTEnv |
| Information about the environment the program is running in. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | phaseGateType { SIGMA_Z =0, S_GATE =1, T_GATE =2 } |
Functions | |
| void | reportState (MultiQubit multiQubit) |
| Print the current state vector of probability amplitudes for a set of qubits to file. More... | |
| void | reportMultiQubitParams (MultiQubit multiQubit) |
| Report metainformation about a set of qubits: number of qubits, number of probability amplitudes. More... | |
| void | rotateAroundAxis (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int rotQubit, REAL angle, Vector unitAxis) |
| Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around a given vector on the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | rotateX (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int rotQubit, REAL angle) |
| Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the X-axis of the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | rotateY (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int rotQubit, REAL angle) |
| Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the Y-axis of the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | rotateZ (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int rotQubit, REAL angle) |
| Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the Z-axis of the Bloch-sphere (also known as a phase shift gate). More... | |
| void | controlledRotateX (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, REAL angle) |
| Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the X-axis of the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | controlledRotateY (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, REAL angle) |
| Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the Y-axis of the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | controlledRotateZ (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, REAL angle) |
| Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the Z-axis of the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | controlledRotateAroundAxis (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, REAL angle, Vector axis) |
| Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around a given vector on the Bloch-sphere. More... | |
| void | sGate (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit S gate. More... | |
| void | tGate (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit T gate. More... | |
| void | getEnvironmentString (QuESTEnv env, MultiQubit multiQubit, char str[200]) |
| void | reportStateToScreen (MultiQubit multiQubit, QuESTEnv env, int reportRank) |
| Print the current state vector of probability amplitudes for a set of qubits to standard out. More... | |
| void | controlledPhaseGate (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int idQubit1, const int idQubit2) |
| Apply the (two-qubit) controlled phase gate, also known as the controlled sigmaZ gate. More... | |
| void | multiControlledPhaseGate (MultiQubit multiQubit, int *controlQubits, int numControlQubits) |
| Apply the multiple-qubit controlled phase gate, also known as the multiple-qubit controlled sigmaZ gate. More... | |
| void | controlledNot (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the controlled not (single control, single target) gate, also known as the c-X, c-sigma-X, c-Pauli-X and c-bit-flip gate. More... | |
| void | createMultiQubit (MultiQubit *multiQubit, int numQubits, QuESTEnv env) |
| Create a MultiQubit object representing a set of qubits. More... | |
| void | destroyMultiQubit (MultiQubit multiQubit, QuESTEnv env) |
| Deallocate a MultiQubit object representing a set of qubits. More... | |
| void | initStateZero (MultiQubit *multiQubit) |
Initialise a set of 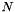 qubits to the classical zero state qubits to the classical zero state 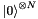 . More... . More... | |
| void | initStatePlus (MultiQubit *multiQubit) |
Initialise a set of 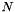 qubits to the plus state qubits to the plus state 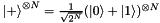 . More... . More... | |
| void | initClassicalState (MultiQubit *multiQubit, long long int stateInd) |
Initialise a set of 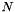 qubits to the classical state with index qubits to the classical state with index stateInd. More... | |
| void | initQuESTEnv (QuESTEnv *env) |
| Initialize QuEST environment. More... | |
| void | closeQuESTEnv (QuESTEnv env) |
| Initialize the QuEST environment. More... | |
| void | syncQuESTEnv (QuESTEnv env) |
| Guarantees that all code up to the given point has been executed on all nodes. More... | |
| int | syncQuESTSuccess (int successCode) |
| Performs a logical AND on all successCodes held by all processes. More... | |
| void | reportQuESTEnv (QuESTEnv env) |
| Report information about the QuEST environment. More... | |
| REAL | calcTotalProbability (MultiQubit multiQubit) |
| Calculate the probability of being in any state by taking the norm of the entire state vector. More... | |
| void | compactUnitary (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int rotQubit, Complex alpha, Complex beta) |
| Apply a single-qubit unitary parameterised by two given complex scalars. More... | |
| void | controlledCompactUnitary (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, Complex alpha, Complex beta) |
| Apply a controlled unitary (single control, single target) parameterised by two given complex scalars. More... | |
| void | unitary (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit, ComplexMatrix2 u) |
| Apply a general single-qubit unitary (including a global phase factor). More... | |
| void | controlledUnitary (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int controlQubit, const int targetQubit, ComplexMatrix2 u) |
| Apply a general controlled unitary (single control, single target), which can include a global phase factor. More... | |
| void | multiControlledUnitary (MultiQubit multiQubit, int *controlQubits, const int numControlQubits, const int targetQubit, ComplexMatrix2 u) |
| Apply a general multiple-control single-target unitary, which can include a global phase factor. More... | |
| void | sigmaX (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit sigma-X (also known as the X, Pauli-X, NOT or bit-flip) gate. More... | |
| void | sigmaY (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit sigma-Y (also known as the Y or Pauli-Y) gate. More... | |
| void | sigmaZ (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit sigma-Z (also known as the Z, Pauli-Z or phase-flip) gate. More... | |
| void | hadamard (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int targetQubit) |
| Apply the single-qubit Hadamard gate. More... | |
| REAL | findProbabilityOfOutcome (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int measureQubit, int outcome) |
| Gives the probability of a specified qubit being measured in the given outcome (0 or 1). More... | |
| REAL | collapseToOutcome (MultiQubit multiQubit, const int measureQubit, int outcome) |
| Updates the state vector to be consistent with measuring the measure qubit in the given outcome (0 or 1), and returns the probability of such a measurement outcome. More... | |
| int | measure (MultiQubit multiQubit, int measureQubit) |
| Measures a single qubit, collapsing it randomly to 0 or 1. More... | |
| int | measureWithStats (MultiQubit multiQubit, int measureQubit, REAL *stateProb) |
| Measures a single qubit, collapsing it randomly to 0 or 1, and additionally gives the probability of that outcome. More... | |
| void | QuESTSeedRandomDefault (void) |
| Seed the Mersenne Twister used for random number generation in the QuEST environment with an example defualt seed. More... | |
| void | QuESTSeedRandom (unsigned long int *seedArray, int numSeeds) |
| Seed the Mersenne Twister used for random number generation in the QuEST environment with a user defined seed. More... | |
Detailed Description
The QuEST library API and objects.
Definition in file QuEST.h.
Typedef Documentation
◆ Complex
◆ ComplexArray
| typedef struct ComplexArray ComplexArray |
Represents an array of complex numbers grouped into an array of real components and an array of coressponding complex components.
◆ ComplexMatrix2
| typedef struct ComplexMatrix2 ComplexMatrix2 |
Represents a 2x2 matrix of complex numbers.
◆ MultiQubit
| typedef struct MultiQubit MultiQubit |
Represents a system of qubits.
Qubits are zero-based and the the first qubit is the rightmost
◆ QuESTEnv
Information about the environment the program is running in.
In practice, this holds info about MPI ranks and helps to hide MPI initialization code
◆ Vector
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ phaseGateType
| enum phaseGateType |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SIGMA_Z | |
| S_GATE | |
| T_GATE | |
Function Documentation
◆ calcTotalProbability()
| REAL calcTotalProbability | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit | ) |
Calculate the probability of being in any state by taking the norm of the entire state vector.
Should be equal to 1.
- Parameters
-
[in] multiQubit object representing a set of qubits
- Returns
- total probability
◆ closeQuESTEnv()
| void closeQuESTEnv | ( | QuESTEnv | env | ) |
Initialize the QuEST environment.
If something needs to be done to set up the execution environment, such as initializing MPI when running in distributed mode, it is handled here
- Parameters
-
[in,out] env object representing the execution environment. A single instance is used for each program
◆ collapseToOutcome()
| REAL collapseToOutcome | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | measureQubit, | ||
| int | outcome | ||
| ) |
Updates the state vector to be consistent with measuring the measure qubit in the given outcome (0 or 1), and returns the probability of such a measurement outcome.
This is effectively performing a measurement and forcing the outcome. This is an irreversible change to the state vector, whereby incompatible states in the state vector are given zero amplitude and the remaining states are renormalised. Exits with error if the given outcome has ~zero probability, and so cannot be collapsed into.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] measureQubit qubit to measure [in] outcome to force the measure qubit to enter
- Returns
- probability of the (forced) measurement outcome
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if measureQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or ifoutcomeis not in {0, 1}, or if the probability ofoutcomeis zero (within machine epsilon)
◆ compactUnitary()
| void compactUnitary | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | rotQubit, | ||
| Complex | alpha, | ||
| Complex | beta | ||
| ) |
Apply a single-qubit unitary parameterised by two given complex scalars.
Given valid complex numbers 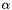 and
and 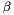 , applies the unitary
, applies the unitary
![\[ U = \begin{pmatrix} \alpha & -\beta^* \\ \beta & \alpha^* \end{pmatrix} \]](form_38.png)
which is general up to a global phase factor.
Valid 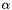 ,
, 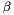 satisfy
satisfy 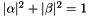 .
.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {U}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_40.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on [in] alpha complex unitary parameter (row 1, column 1) [in] beta complex unitary parameter (row 2, column 1)
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or ifalpha,betadon't satisfy |alpha|^2+ |beta|^2= 1.
Referenced by rotateAroundAxis().
◆ controlledCompactUnitary()
| void controlledCompactUnitary | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| Complex | alpha, | ||
| Complex | beta | ||
| ) |
Apply a controlled unitary (single control, single target) parameterised by two given complex scalars.
Given valid complex numbers 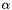 and
and 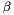 , applies the two-qubit unitary
, applies the two-qubit unitary
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\ & & \alpha & -\beta^* \\ & & \beta & \alpha^* \end{pmatrix} \]](form_41.png)
to the control and target qubits. Valid 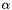 ,
, 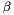 satisfy
satisfy 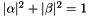 . The target unitary is general up to a global phase factor.
. The target unitary is general up to a global phase factor.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$U_{\alpha, \beta}$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_42.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit apply the target unitary if this qubit has value 1 [in] targetQubit qubit on which to apply the target unitary [in] alpha complex unitary parameter (row 1, column 1) [in] beta complex unitary parameter (row 2, column 1)
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal, or ifalpha,betadon't satisfy |alpha|^2+ |beta|^2= 1.
Referenced by controlledRotateAroundAxis().
◆ controlledNot()
| void controlledNot | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the controlled not (single control, single target) gate, also known as the c-X, c-sigma-X, c-Pauli-X and c-bit-flip gate.
This applies sigmaX to the target qubit if the control qubit has value 1. This effects the two-qubit unitary
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\\ & & & 1 \\ & & 1 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_24.png)
on the control and target qubits.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, -.5); \draw (-2,0) -- (2, 0); \draw (0, 0) circle (.5); \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_25.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit nots the target if this qubit is 1 [in] targetQubit qubit to not
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or are equal.
◆ controlledPhaseGate()
| void controlledPhaseGate | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | idQubit1, | ||
| const int | idQubit2 | ||
| ) |
Apply the (two-qubit) controlled phase gate, also known as the controlled sigmaZ gate.
For each state, if both input qubits have value one, multiply the amplitude of that state by -1. This applies the two-qubit unitary:
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\\ & & 1 \\ & & & -1 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_20.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {idQubit1}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {idQubit2}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 0); \draw (-2,0) -- (2, 0); \draw[fill=black] (0, 0) circle (.2); \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_21.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] idQubit1,idQubit2 qubits to operate upon
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if idQubit1oridQubit2are outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or are equal
◆ controlledRotateAroundAxis()
| void controlledRotateAroundAxis | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle, | ||
| Vector | axis | ||
| ) |
Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around a given vector on the Bloch-sphere.
The vector must not be zero (else an error is thrown), but needn't be unit magnitude.
For angle 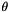 and axis vector
and axis vector 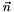 , applies
, applies 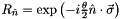 to states where the target qubit is 1 (
to states where the target qubit is 1 ( 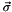 is the vector of Pauli matrices).
is the vector of Pauli matrices).
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_{\hat{n}}(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_13.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit qubit with value 1 in the rotated states [in] targetQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate in radians [in] axis vector around which to rotate (can be non-unit; will be normalised)
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal or ifaxisis the zero vector
Definition at line 122 of file QuEST.cpp.
References controlledCompactUnitary(), Complex::imag, Complex::real, Vector::x, Vector::y, and Vector::z.
Referenced by controlledRotateX(), controlledRotateY(), and controlledRotateZ().
◆ controlledRotateX()
| void controlledRotateX | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the X-axis of the Bloch-sphere.
The target qubit is rotated in states where the control qubit has value 1.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_x(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_7.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit qubit which has value 1 in the rotated states [in] tagretQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate the target qubit in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal.
Definition at line 135 of file QuEST.cpp.
References controlledRotateAroundAxis().
◆ controlledRotateY()
| void controlledRotateY | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the Y-axis of the Bloch-sphere.
The target qubit is rotated in states where the control qubit has value 1.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_y(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_8.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit qubit which has value 1 in the rotated states [in] tagretQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate the target qubit in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal.
Definition at line 141 of file QuEST.cpp.
References controlledRotateAroundAxis().
◆ controlledRotateZ()
| void controlledRotateZ | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Applies a controlled rotation by a given angle around the Z-axis of the Bloch-sphere.
The target qubit is rotated in states where the control qubit has value 1.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_z(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_9.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit qubit which has value 1 in the rotated states [in] tagretQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate the target qubit in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal.
Definition at line 147 of file QuEST.cpp.
References controlledRotateAroundAxis().
◆ controlledUnitary()
| void controlledUnitary | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | controlQubit, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| ComplexMatrix2 | u | ||
| ) |
Apply a general controlled unitary (single control, single target), which can include a global phase factor.
The given unitary is applied to the target qubit if the control qubit has value 1, effecting the two-qubit unitary
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\ & & u_{00} & u_{01}\\ & & u_{10} & u_{11} \end{pmatrix} \]](form_43.png)
on the control and target qubits.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {control}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {U}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_44.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubit apply unitary if this qubit is 1 [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on [in] u single-qubit unitary matrix to apply
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if either controlQubitortargetQubitare outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits) or are equal, or ifuis not unitary.
◆ createMultiQubit()
| void createMultiQubit | ( | MultiQubit * | multiQubit, |
| int | numQubits, | ||
| QuESTEnv | env | ||
| ) |
Create a MultiQubit object representing a set of qubits.
Allocate space for state vector of probability amplitudes, including space for temporary values to be copied from one other chunk if running the distributed version. Define properties related to the size of the set of qubits. initStateZero should be called after this to initialise the qubits to the zero state.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit a pointer to an object representing the set of qubits [in] numQubits number of qubits in the system [in] env object representing the execution environment (local, multinode etc)
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if numQubits<= 0
◆ destroyMultiQubit()
| void destroyMultiQubit | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| QuESTEnv | env | ||
| ) |
Deallocate a MultiQubit object representing a set of qubits.
Free memory allocated to state vector of probability amplitudes, including temporary vector for values copied from another chunk if running the distributed version.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object to be deallocated [in] env object representing the execution environment (local, multinode etc)
◆ findProbabilityOfOutcome()
| REAL findProbabilityOfOutcome | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | measureQubit, | ||
| int | outcome | ||
| ) |
Gives the probability of a specified qubit being measured in the given outcome (0 or 1).
This performs no actual measurement and does not change the state of the qubits.
- Parameters
-
[in] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] measureQubit qubit to study [in] outcome for which to find the probability of the qubit being measured in
- Returns
- probability of qubit measureQubit being measured in the given outcome
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if measureQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or ifoutcomeis not in {0, 1}.
◆ getEnvironmentString()
| void getEnvironmentString | ( | QuESTEnv | env, |
| MultiQubit | multiQubit, | ||
| char | str[200] | ||
| ) |
◆ hadamard()
| void hadamard | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit Hadamard gate.
This takes 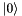 to
to 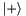 and
and 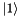 to
to 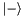 , and is equivalent to a rotation of
, and is equivalent to a rotation of 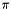 around the x-axis then
around the x-axis then 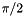 about the y-axis on the Bloch-sphere. I.e.
about the y-axis on the Bloch-sphere. I.e.
![\[ \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 1 & -1 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_58.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {H}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_59.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
◆ initClassicalState()
| void initClassicalState | ( | MultiQubit * | multiQubit, |
| long long int | stateInd | ||
| ) |
Initialise a set of 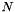 qubits to the classical state with index
qubits to the classical state with index stateInd.
Note  has
has stateInd 0,  has
has stateInd 1,  has
has stateInd 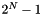 , etc. Subsequent calls to getProbEl will yield 0 for all indices except
, etc. Subsequent calls to getProbEl will yield 0 for all indices except stateInd.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit a pointer to the object representing the set of qubits to be initialised [in] stateInd the index (0 to the number of amplitudes, exclusive) of the state to give probability 1
◆ initQuESTEnv()
| void initQuESTEnv | ( | QuESTEnv * | env | ) |
Initialize QuEST environment.
If something needs to be done to set up the execution environment, such as initializing MPI when running in distributed mode, it is handled here
- Parameters
-
[in,out] env object representing the execution environment. A single instance is used for each program
◆ initStatePlus()
| void initStatePlus | ( | MultiQubit * | multiQubit | ) |
Initialise a set of 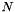 qubits to the plus state
qubits to the plus state 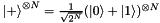 .
.
This is the product state of 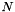 qubits where every classical state is uniformly populated with real coefficient
qubits where every classical state is uniformly populated with real coefficient 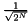 . This is equivalent to applying a Hadamard to every qubit in the zero state:
. This is equivalent to applying a Hadamard to every qubit in the zero state: 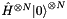
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit a pointer to the object representing the set of qubits to be initialised
◆ initStateZero()
| void initStateZero | ( | MultiQubit * | multiQubit | ) |
Initialise a set of 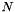 qubits to the classical zero state
qubits to the classical zero state 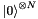 .
.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit a pointer to the object representing the set of all qubits to initialise
◆ measure()
| int measure | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| int | measureQubit | ||
| ) |
Measures a single qubit, collapsing it randomly to 0 or 1.
Outcome probabilities are weighted by the state vector, which is irreversibly changed after collapse to be consistent with the outcome.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] measureQubit qubit to measure
- Returns
- the measurement outcome, 0 or 1
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if measureQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits)
◆ measureWithStats()
| int measureWithStats | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| int | measureQubit, | ||
| REAL * | stateProb | ||
| ) |
Measures a single qubit, collapsing it randomly to 0 or 1, and additionally gives the probability of that outcome.
Outcome probabilities are weighted by the state vector, which is irreversibly changed after collapse to be consistent with the outcome.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] measureQubit qubit to measure [out] stateProb a pointer to a REAL which is set to the probability of the occurred outcome
- Returns
- the measurement outcome, 0 or 1
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if measureQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits)
◆ multiControlledPhaseGate()
| void multiControlledPhaseGate | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| int * | controlQubits, | ||
| int | numControlQubits | ||
| ) |
Apply the multiple-qubit controlled phase gate, also known as the multiple-qubit controlled sigmaZ gate.
For each state, if all control qubits have value one, multiply the amplitude of that state by -1. This applies the many-qubit unitary:
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\\ & & \ddots \\ & & & 1 \\ & & & & -1 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_22.png)
on the control qubits.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 2) {controls}; \node[draw=none] at (0, 6) {$\vdots$}; \draw (0, 5) -- (0, 4); \draw (-2, 4) -- (2, 4); \draw[fill=black] (0, 4) circle (.2); \draw (0, 4) -- (0, 2); \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 0); \draw (-2,0) -- (2, 0); \draw[fill=black] (0, 0) circle (.2); \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_23.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubits array of input qubits [in] numControlQubits number of input qubits
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if numControlQubitsis outside [1,multiQubit.numQubits)
◆ multiControlledUnitary()
| void multiControlledUnitary | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| int * | controlQubits, | ||
| const int | numControlQubits, | ||
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| ComplexMatrix2 | u | ||
| ) |
Apply a general multiple-control single-target unitary, which can include a global phase factor.
Any number of control qubits can be specified, and if all have value 1, the given unitary is applied to the target qubit. This effects the many-qubit unitary
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ & 1 \\\ & & \ddots \\ & & & u_{00} & u_{01}\\ & & & u_{10} & u_{11} \end{pmatrix} \]](form_45.png)
on the control and target qubits. The given 2x2 ComplexMatrix must be unitary, otherwise an error is thrown.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 3) {controls}; \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \node[draw=none] at (0, 6) {$\vdots$}; \draw (0, 5) -- (0, 4); \draw (-2, 4) -- (2, 4); \draw[fill=black] (0, 4) circle (.2); \draw (0, 4) -- (0, 2); \draw (-2, 2) -- (2, 2); \draw[fill=black] (0, 2) circle (.2); \draw (0, 2) -- (0, 1); \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {U}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_46.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] controlQubits applies unitary if all qubits in this array equal 1 [in] numControlQubits number of control qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on [in] u single-qubit unitary matrix to apply
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if numControlQubitsis outside [1,multiQubit.numQubits]), or if any qubit index (targetQubitor one incontrolQubits) is outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits]), or ifcontrolQubitscontainstargetQubit, or ifuis not unitary.
◆ QuESTSeedRandom()
| void QuESTSeedRandom | ( | unsigned long int * | seedArray, |
| int | numSeeds | ||
| ) |
Seed the Mersenne Twister used for random number generation in the QuEST environment with a user defined seed.
This function uses the mt19937 init_by_array function with numSeeds keys supplied by the user. Subsequent calls to mt19937 genrand functions will use this seeding. For a multi process code, the same seed is given to all process, therefore this seeding is only appropriate to use for functions such as measure where all processes require the same random value.
- Parameters
-
[in] seedArray Array of integers to use as seed. This allows the MT to be initialised with more than a 32-bit integer if required [in] numSeeds Length of seedArray
For more information about the MT, see http://www.math.sci.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~m-mat/MT/MT2002/emt19937ar.html
Seed the Mersenne Twister used for random number generation in the QuEST environment with a user defined seed.
Definition at line 231 of file QuEST.cpp.
References init_by_array().
◆ QuESTSeedRandomDefault()
| void QuESTSeedRandomDefault | ( | void | ) |
Seed the Mersenne Twister used for random number generation in the QuEST environment with an example defualt seed.
This default seeding function uses the mt19937 init_by_array function with three keys – time, pid and hostname. Subsequent calls to mt19937 genrand functions will use this seeding. For a multi process code, the same seed is given to all process, therefore this seeding is only appropriate to use for functions such as measure where all processes require the same random value.
For more information about the MT, see http://www.math.sci.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~m-mat/MT/MT2002/emt19937ar.html
Definition at line 206 of file QuEST.cpp.
References hashString(), and init_by_array().
◆ reportMultiQubitParams()
| void reportMultiQubitParams | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit | ) |
Report metainformation about a set of qubits: number of qubits, number of probability amplitudes.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of qubits [in] env object representing the execution environment (local, multinode etc)
Definition at line 80 of file QuEST.cpp.
References MultiQubit::chunkId, MultiQubit::numChunks, and MultiQubit::numQubits.
◆ reportQuESTEnv()
| void reportQuESTEnv | ( | QuESTEnv | env | ) |
Report information about the QuEST environment.
- Parameters
-
[in] env object representing the execution environment. A single instance is used for each program
◆ reportState()
| void reportState | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit | ) |
Print the current state vector of probability amplitudes for a set of qubits to file.
File format:
real, imag realComponent1, imagComponent1 realComponent2, imagComponent2 ... realComponentN, imagComponentN
File naming convention:
For each node that the program runs on, a file 'state_rank_[node_rank].csv' is generated. If there is more than one node, ranks after the first do not include the header
real, imag
so that files are easier to combine.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of qubits
Definition at line 62 of file QuEST.cpp.
References MultiQubit::chunkId, ComplexArray::imag, MultiQubit::numAmps, ComplexArray::real, and MultiQubit::stateVec.
◆ reportStateToScreen()
| void reportStateToScreen | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| QuESTEnv | env, | ||
| int | reportRank | ||
| ) |
Print the current state vector of probability amplitudes for a set of qubits to standard out.
For debugging purposes. Each rank should print output serially. Only print output for systems <= 5 qubits
◆ rotateAroundAxis()
| void rotateAroundAxis | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | rotQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle, | ||
| Vector | unitAxis | ||
| ) |
Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around a given vector on the Bloch-sphere.
- The vector must not be zero (else an error is thrown), but needn't be unit magnitude.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] rotQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate in radians [in] axis vector around which to rotate
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if rotQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or ifaxisis the zero vector
Definition at line 91 of file QuEST.cpp.
References compactUnitary(), Complex::imag, Complex::real, Vector::x, Vector::y, and Vector::z.
Referenced by rotateX(), rotateY(), and rotateZ().
◆ rotateX()
| void rotateX | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | rotQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the X-axis of the Bloch-sphere.
For angle 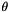 , applies
, applies
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} \cos\theta/2 & -i \sin \theta/2\\ -i \sin \theta/2 & \cos \theta/2 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_1.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {rot}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_x(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_2.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] rotQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if rotQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
Definition at line 104 of file QuEST.cpp.
References rotateAroundAxis().
◆ rotateY()
| void rotateY | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | rotQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the Y-axis of the Bloch-sphere.
For angle 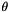 , applies
, applies
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} \cos\theta/2 & \sin \theta/2\\ \sin \theta/2 & \cos \theta/2 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_3.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {rot}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_y(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_4.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] rotQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if rotQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
Definition at line 110 of file QuEST.cpp.
References rotateAroundAxis().
◆ rotateZ()
| void rotateZ | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | rotQubit, | ||
| REAL | angle | ||
| ) |
Rotate a single qubit by a given angle around the Z-axis of the Bloch-sphere (also known as a phase shift gate).
For angle 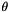 , applies
, applies
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} \exp(-i \theta/2) & 0 \\ 0 & \exp(i \theta/2) \end{pmatrix} \]](form_5.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {rot}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$R_z(\theta)$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_6.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] rotQubit qubit to rotate [in] angle angle by which to rotate in radians
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if rotQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
Definition at line 116 of file QuEST.cpp.
References rotateAroundAxis().
◆ sGate()
| void sGate | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit S gate.
This is a rotation of 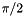 around the Z-axis on the Bloch sphere, or the unitary:
around the Z-axis on the Bloch sphere, or the unitary:
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & i \end{pmatrix} \]](form_15.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {S}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_16.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate upon
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits)
Definition at line 158 of file QuEST.cpp.
References phaseGate(), and S_GATE.
◆ sigmaX()
| void sigmaX | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit sigma-X (also known as the X, Pauli-X, NOT or bit-flip) gate.
This is a rotation of 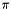 around the x-axis on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
around the x-axis on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_48.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (2, 0); \draw (0, 0) circle (.5); \draw (0, .5) -- (0, -.5); \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_49.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
◆ sigmaY()
| void sigmaY | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit sigma-Y (also known as the Y or Pauli-Y) gate.
This is a rotation of 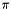 around the Y-axis on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
around the Y-axis on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 0 & -i \\ i & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_50.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$\sigma_y$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_51.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
◆ sigmaZ()
| void sigmaZ | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit sigma-Z (also known as the Z, Pauli-Z or phase-flip) gate.
This is a rotation of 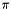 around the Z-axis (a phase shift) on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
around the Z-axis (a phase shift) on the Bloch sphere. I.e.
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} \]](form_52.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {$\sigma_z$}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_53.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits).
Definition at line 153 of file QuEST.cpp.
References phaseGate(), and SIGMA_Z.
◆ syncQuESTEnv()
| void syncQuESTEnv | ( | QuESTEnv | env | ) |
Guarantees that all code up to the given point has been executed on all nodes.
- Parameters
-
[in] env object representing the execution environment. A single instance is used for each program
◆ syncQuESTSuccess()
| int syncQuESTSuccess | ( | int | successCode | ) |
Performs a logical AND on all successCodes held by all processes.
If any one process has a zero successCode all processes will return a zero success code.
- Parameters
-
[in] env object representing the execution environment. A single instance is used for each program [in] successCode 1 if process task succeeded, 0 if process task failed
- Returns
- 1 if all processes succeeded, 0 if any one process failed
◆ tGate()
| void tGate | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit | ||
| ) |
Apply the single-qubit T gate.
This is a rotation of 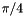 around the Z-axis on the Bloch sphere, or the unitary:
around the Z-axis on the Bloch sphere, or the unitary:
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & \exp\left(i \frac{\pi}{4}\right) \end{pmatrix} \]](form_18.png)
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {T}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_19.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate upon
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits)
Definition at line 163 of file QuEST.cpp.
References phaseGate(), and T_GATE.
◆ unitary()
| void unitary | ( | MultiQubit | multiQubit, |
| const int | targetQubit, | ||
| ComplexMatrix2 | u | ||
| ) |
Apply a general single-qubit unitary (including a global phase factor).
The passed 2x2 ComplexMatrix must be unitary, otherwise an error is thrown.
![\[ \setlength{\fboxrule}{0.01pt} \fbox{ \begin{tikzpicture}[scale=.5] \node[draw=none] at (-3.5, 0) {target}; \draw (-2,0) -- (-1, 0); \draw (1, 0) -- (2, 0); \draw (-1,-1)--(-1,1)--(1,1)--(1,-1)--cycle; \node[draw=none] at (0, 0) {U}; \end{tikzpicture} } \]](form_40.png)
- Parameters
-
[in,out] multiQubit object representing the set of all qubits [in] targetQubit qubit to operate on [in] u unitary matrix to apply
- Exceptions
-
exitWithError if targetQubitis outside [0,multiQubit.numQubits), or matrixuis not unitary.
 1.8.14
1.8.14